Stripe Actuators
Bilaminar, flexing actuators featuring:
- large deflections
- useful blocking forces
- surfaces protected from environmental hazards
- electrical leads / no leads
- custom dimensions available
- competitive pricing
- fast delivery
Typical Applications of Stripe Actuators
Use Stripe actuators in applications that demand sensitivity or a large response:
- needle control in textile weaving
- Braille machines
- accelerometers
- opening / closing valves
- small-volume pumping devices
- switching applications - touch switches -
making / breaking electrical contact - cooling devices for electronics (no electromagnetic noise)
For proper use, Stripe Actuators must be secured to a solid surface. Visit our Securing a Stripe Actuator; Connecting Electrical Leads resource for more information and a detailed procedure list for your convenience.
Stripe Actuators - APC no longer stocks these actuators. Send APC your requirements for review. Minumum order quantities will be 100 pieces with an approximate lead time of 12 weeks.
| APCI Catalog No. |
Product Description |
Dimensions (mm) | Free Length (mm) |
Total Deflection (mm) |
Blocking Force (N) |
Resonance Freq. (Hz) |
Capacitance (pF) |
|||
| Length | Width | Thk. | ||||||||
Deflections and blocking forces measured at driving voltage of 150 V (maximum) in direction of polarization.
Operating temperature: -25°C to 70°C; storage temperature: -40°C to 85°C.
Dimensional Tolerances: Length ±0.25 mm, Width ±0.25 mm, Thickness ±0.10 mm.
Custom Design and Engineering Services
If the dimensions or performance characteristics of standard Stripe actuators do not fit your needs, we can custom-manufacture these actuators to your specifications. Before you request custom products, however, we recommend you evaluate standard Stripe actuators for your application by varying the free length, the method of mounting, and/or the applied voltage. The relationships discussed below should also help with any evaluation of APC's Stripe Actuators. If you find that standard Stripe actuators will not provide the performance you need, simply contact an APCI representative to discuss alternatives.
Background Information
A flexing or bending actuator is designed to produce a relatively large mechanical deflection in response to an electrical signal. Two thin strips of piezoelectric ceramic are bonded together, usually with the direction of polarization coinciding, and are electrically connected in parallel. When electrical input is applied, one ceramic layer expands and the other contracts, causing the actuator to flex. Deflections are large, but blocking forces are low, relative to forces developed by stack actuators. Parallel electrical configuration ensures high sensitivity to input; bias voltage circuitry can prolong the life of the actuator by eliminating the potential for depolarizing the ceramic layers.
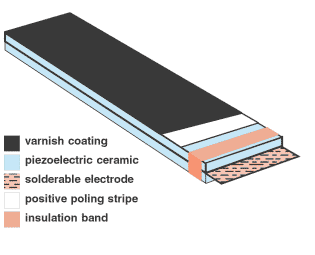
- Proprietary layering technology increases flexibility, allows greater deflection
- Parallel electrical configuration of ceramic layers ensures high sensitivity to input; compatible with bias voltage circuitry that eliminates the potential for depolarizing the ceramic layers
- Varnish layer electrically insulates surface, protects from humidity, dust and other hazards
- White stripe identifies positive surface
- Solderable electrode bonded between plates
- Thickness tolerance for part without applied coatings
Advanced layering technologies have enabled APC International, Ltd. to develop the Stripe actuator, a flexing actuator that achieves greater deflections than conventional designs. Stripe actuators derive their name from a white stripe that denotes the positive surface.
A standard sized Stripe actuator secured in a cantilever mounting configuration has a deflection range of up to >2.5 mm, in response to a 150 V (maximum) input. If deflection is blocked, a Stripe actuator will develop a useable force. The relationships discussed below can assist you in determining the deflections and blocking forces of these actuators.
Vulnerable surfaces of a Stripe actuator are coated with a special varnish that electrically insulates the surface and protects it from humidity, dust, and other hazards that can shorten the working lifetime of the actuator. A solderable electrode is bonded between the plates.
Performance of Stripe Actuators
Use this information to determine what combinations of free length, thickness, width, and applied voltage will provide the deflection or force you need from a Stripe actuator. Measured values for Stripe actuators will be within ±30% of the calculated values.
Variables Affecting the Performance of a Stripe Actuator
| 1) | dimensions - total length (ltot) free length (lf ) width (w) thickness (h) | |
| 2) | deflection | |
| 3) | cantilever mounting: bonded attachment | |
| 4) | cantilever mounting: point attachment | |
| 5) | parallel drive - (high sensitivity to input) 50 V max | |
| 6) | bias drive - (eliminates potential for depolarization) 150 VDC bias max | |
Calculations for Estimating Performance Characteristics of a Stripe Actuator
| Characteristic | Calculation | Result |
| Total Deflection | 2.2 x 10-6x ( [lf]2 / [h]2 ) ( [V] ) | mm |
| Compliance | 26.4 x10-5 x ([lf ]3/ ( [w] ) ( [h]3 ) | -- |
| Blocking Force | [deflection] / [compliance] | N |
| Resonance Frequency | 3.2 x 105x ( [h] / [lf]2 ) | Hz |
lf = free length of actuator
h = thickness of actuator
w = width of actuator
V = voltage (150 V maximum)
Blocking Forces and Half-Deflections
Through composite layering technologies, APC International, Ltd. has developed the Stripe actuator, a flexional piezoelectric ceramic actuator that achieves greater deflections than conventional bilaminar actuators. In conventional cantilever mounting configurations, the four standard sizes of Stripe actuators provide total deflections ranging from > 1.1 mm to 2.6mm, in response to the maximum input voltage. The design of a Stripe actuator maximizes deflection, but, if movement is blocked, the actuator will develop a useable force, up to > 0.60N. The relationships in can be used to estimate the deflection and blocking force for a Stripe actuator that is mounted with a free length other than listed in. Observed values will be within ±30% of calculated values.
Stripe actuators derive their name from a white stripe that identifies the positive surface. Both plates of a Stripe actuator are polarized in the same direction (parallel bilaminar element), and a solderable electrode is bonded between the plates. Vulnerable surfaces of a Stripe actuator are coated with a special varnish that electrically insulates the surface and protects it from humidity, dust, and other hazards that can shorten the working lifetime of an unprotected actuator.
A piezoelectric actuator responds with a mechanical displacement (stroke), when stimulated by an electrical signal or, if displacement is prevented (blocked), with a force (blocking force) the magnitude of which is determined by the stiffness imparted by the design of the actuator. There is an approximately linear relationship between input signal and actuator response, either as a stroke or as a blocking force.